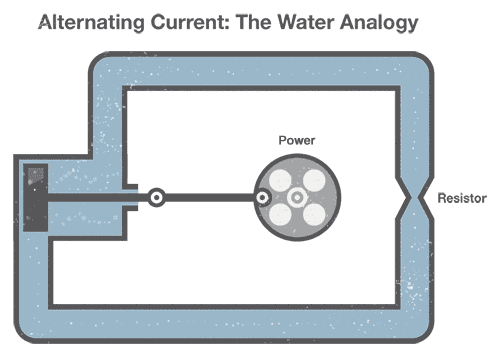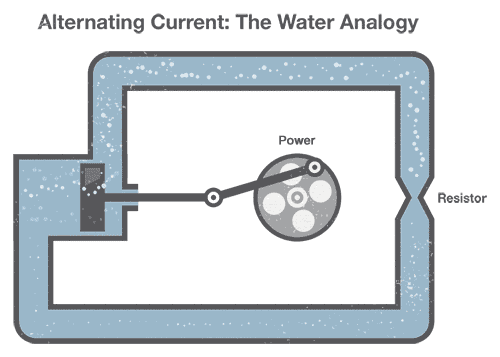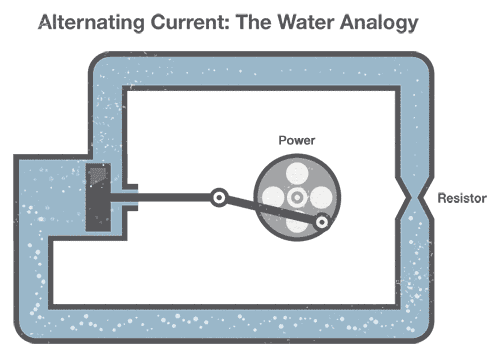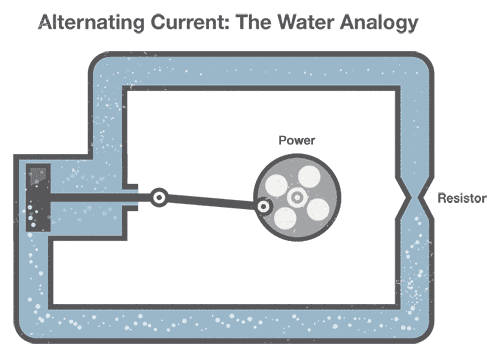
AC (alternating current)
Student Learning Objectives
- Describe how alternating current is produced
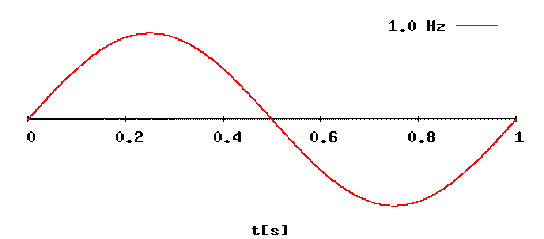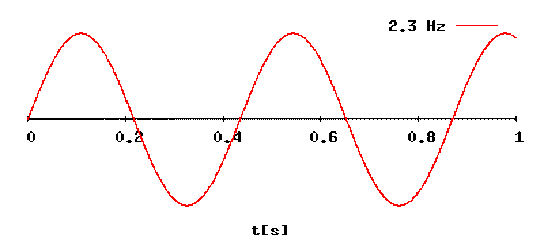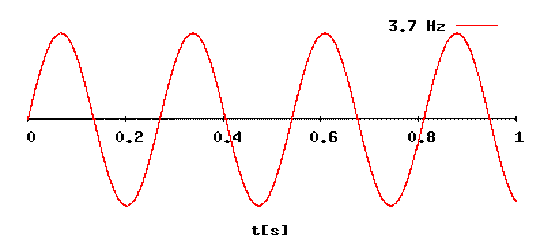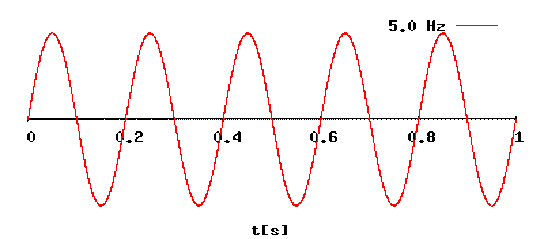
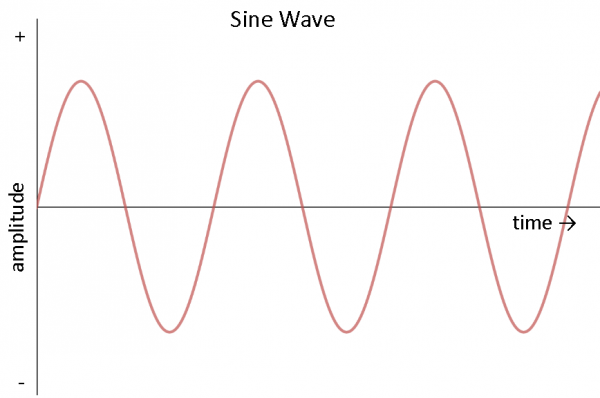
- Demonstrate a sine wave
- Determine the frequency, period, and amplitude of a sine wave
- Calculate and explain what is meant by the RMS value of a sine wave
- List multiple advantages and disadvantages of AC
What are the different ways that electricity can be produced?
Why do we use both AC and DC?
Ohm's Law and Transformers
At higher voltages, the same power could be transmitted at much lower current, which meant less power lost due to resistance in the wires. As a result, large power plants could be located many miles away and service a greater number of people and buildings.
Why do we use both AC and DC?
Ohm's Law and Transformers
At higher voltages, the same power could be transmitted at much lower current, which meant less power lost due to resistance in the wires. As a result, large power plants could be located many miles away and service a greater number of people and buildings.