A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the information the schematic is intended to convey, and may add unrealistic elements that aid comprehension.
|
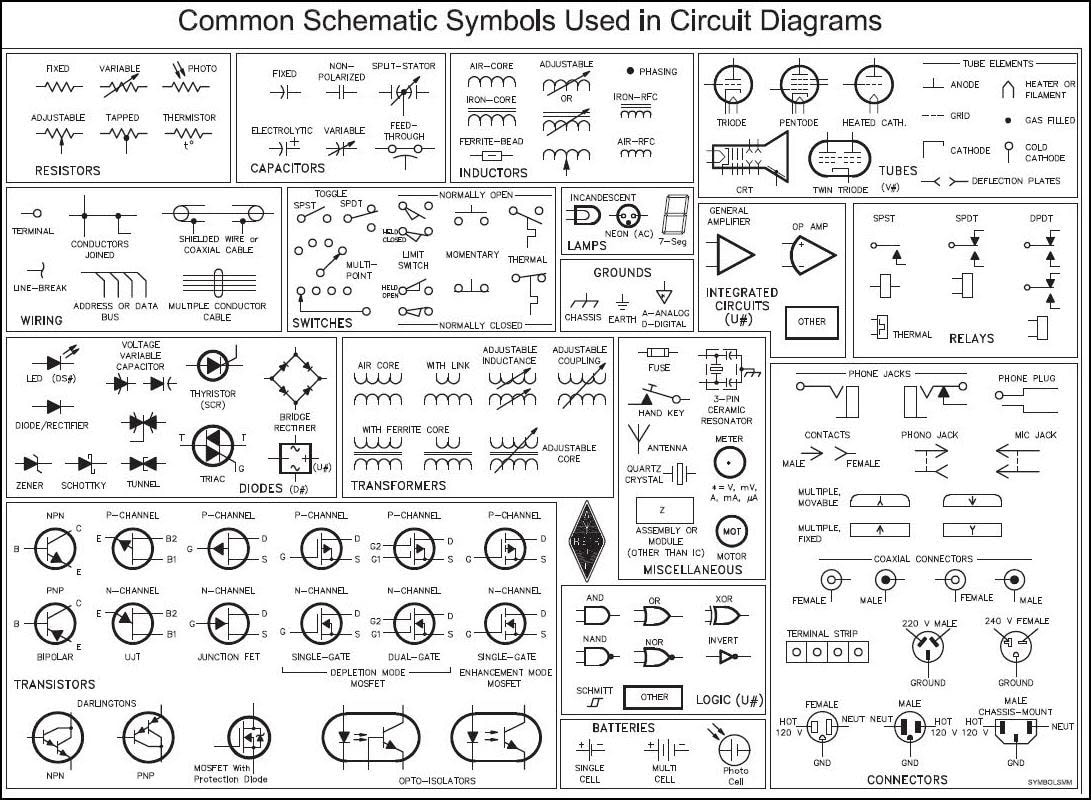
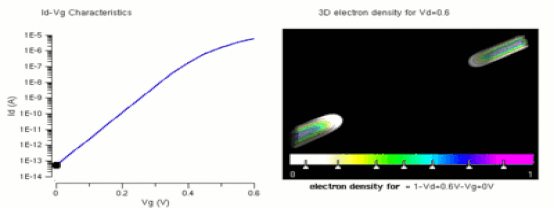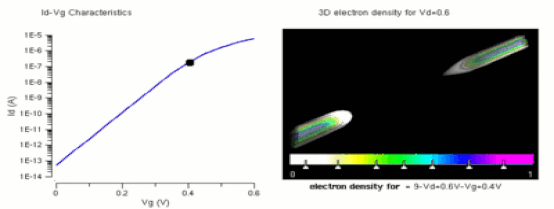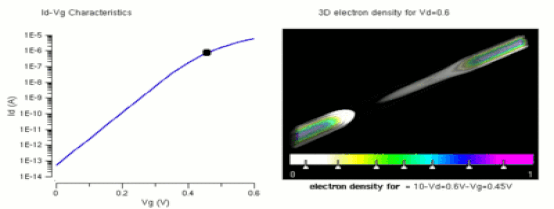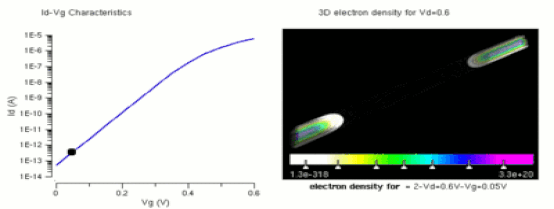
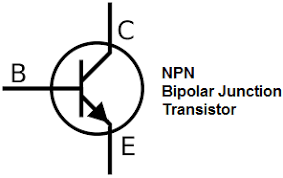
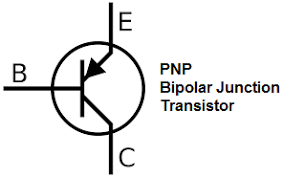
TRANSISTORS Many consider it to be one of the greatest inventions of the 20th century A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems. Julius Edgar Lilienfeld patented a field-effect transistor in 1926[1] but it was not possible to actually construct a working device at that time. The first practically implemented device was a point-contact transistor invented in 1947 by American physicists John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley. The transistor revolutionized the field of electronics, and paved the way for smaller and cheaperradios, calculators, and computers, among other things. The transistor is on the list of IEEE milestones in electronics,[2] and Bardeen, Brattain, and Shockley shared the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for their achievement.[3] |
|
SCR (RECITFIERS)
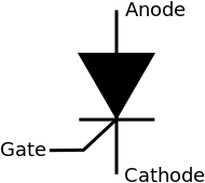
A silicon controlled rectifier or semiconductor-controlled rectifier is a four-layer solid-state current-controlling device. The principle of four layer p-n-p-n switching was developed by Moll, Tanenbaum, Goldey and Holonyak of Bell Laboratories in 1956.[1] The practical demonstration of silicon controlled switching and detailed theoretical behavior of a device in agreement with the experimental results was presented by Dr Ian M. Mackintosh of Bell Laboratories in January 1958.[2][3] The name "silicon controlled rectifier" is General Electric's trade name for a type of thyristor. The SCR was developed by a team of power engineers led by Gordon Hall[4] and commercialized by Frank W. "Bill" Gutzwiller in 1957. |